Understanding Search Engines and their Algorithms
Introduction
Search engines represent sophisticated software systems meticulously crafted to assist users in locating information across the vast landscape of the internet. They achieve this by meticulously indexing copious amounts of web content, determining relevance to a user’s query, and presenting the most pertinent results. These engines employ intricate algorithms to perform these tasks efficiently. Prominent search engine examples include Google, Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo.
What Do Search Engines Do?
Search engines are powerful digital aids for users in traversing the expansive realms of the internet. Their operation entails the meticulous indexing of web content and the application of intricate algorithms to deliver results that align with users’ queries. Google, Bing, and Yahoo are noteworthy exemplars. Users input keywords or phrases, prompting the search engine to explore its extensive database for a collection of web pages thoughtfully ranked according to their relevance. Essentially, search engines serve as gateways to the wealth of information accessible online, providing users with the answers they seek.
How Do Search Engines Operate?
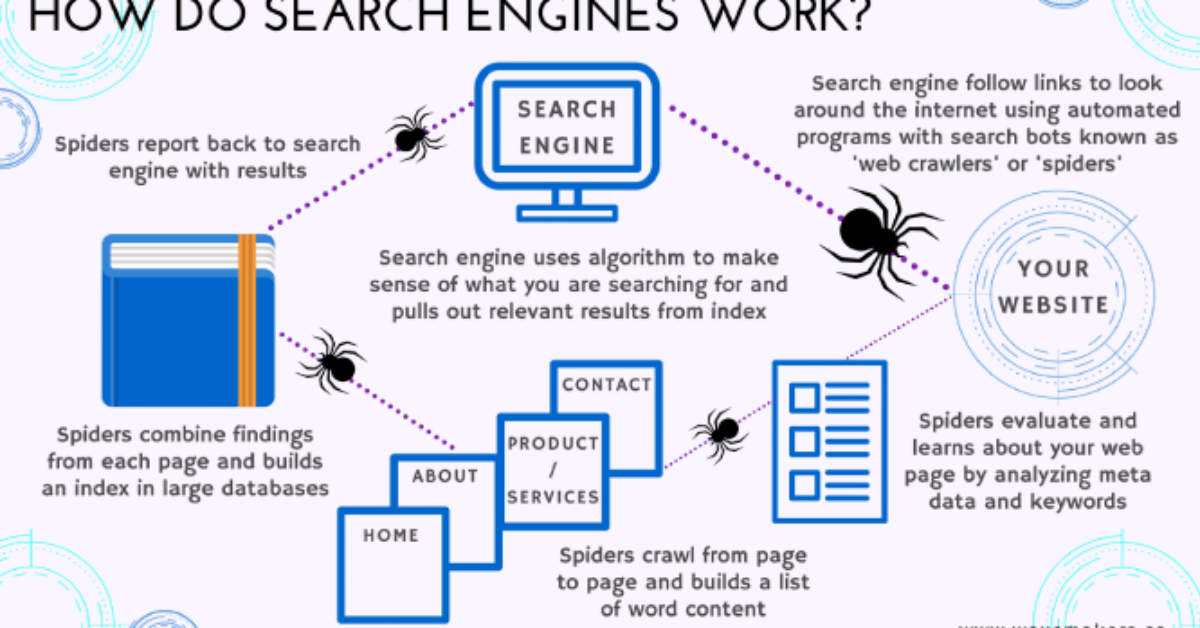
Search engines engage in a multifaceted process, commencing with web crawling, where automated bots traverse the web to index content. When a user inputs a search query, algorithms come into play to rank web pages based on their relevance. Keyword matching, user location, and content quality contribute to the outcomes. These algorithms also consider user interactions, such as clicks and engagement. Search engines like Google persistently update and refine their algorithms to provide precise and valuable search outcomes, connecting users with their desired information.
The Significance of Search Engine Algorithms
Search engine algorithms represent the covert architects of the web’s organization. They evaluate and order web pages based on various factors: content quality, keywords, user behaviour, and backlinks. These algorithms aim to give users the most pertinent, credible, and high-quality query results. Constantly evolving, they incorporate advanced techniques like natural language processing and personalization to better comprehend user intent and deliver an optimized search experience.
Prominent Search Engines and Their Algorithms
Distinguished search engines, including Google, Bing, and Yahoo, employ distinctive algorithms to dispense search results. Google relies on the PageRank algorithm, prioritizing authoritative backlinks and content quality. Bing uses the BingRank algorithm, emphasizing keyword relevance and click-through rates. Although underpinned by Bing’s index, Yahoo employs its unique ranking algorithms, including the HITS (Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search) algorithm. Each search engine’s algorithms influence the character of their search outcomes, offering diverse experiences to users seeking online information.
How Do Algorithms Determine Search Result Rankings?
Algorithms for sorting search results scrutinize many factors to gauge relevance and quality. They consider keyword matching, content quality, backlinks, user engagement, and the user’s geographical location. Advanced algorithms, such as Google’s, leverage natural language processing to grasp the context and intent of a query. User feedback, such as clicks and dwell time (the duration a user remains on a page), also exerts influence. These algorithms perpetually evolve, honing their capacity to present users with the most suitable search outcomes.
Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental components of search engines and their algorithms:

- Crawling: Search engines employ automated programs known as web crawlers (or spiders) to navigate the web, uncovering new web pages. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, perpetually building an index of the discovered content.
- Indexing: The information amassed from web pages is stored within a colossal database designated as an index. This index encompasses page content details, such as text, images, and metadata. Factors like page speed, mobile friendliness, and security are also considered during indexing.
- Ranking Algorithms: When a user submits a search query, the search engine invokes a ranking algorithm to determine the sequence in which search results are presented. Google, for instance, employs the intricate PageRank algorithm, considering variables like the number and quality of backlinks, content relevance, and the user’s location when ranking web pages.
- Keyword Matching: Search engines use keyword matching to recognize relevant pages. When a user enters a search query, the search engine scans for pages that encompass the exact keywords or their synonyms.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Certain search engines, like Google, implement NLP to comprehend a query’s meaning better. This enables them to provide more pertinent results by grasping the context and intent behind a search.
- Personalization: Search engines might personalize results based on a user’s search history, location, and other considerations. This personalization can yield different outcomes for distinct users.
- User Feedback: User feedback influences search engine rankings, including clicks and dwell time. If users consistently click on a particular result, the search engine interprets it as more relevant and may elevate its ranking.
- Algorithm Updates: Search engines routinely revise their algorithms to enhance search quality and thwart manipulation. Google, for instance, releases frequent updates like Panda, Penguin, and BERT to refine its search outcomes.
- Paid Search Results: Search engines commonly display paid advertisements alongside organic search results. Advertisers bid on keywords, and their ads appear when they are searched. Paid results are typically labeled as such and are separate from organic results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the intricate domain of search engines and their algorithms has unveiled the remarkable complexities underpinning our digital information landscape. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamic and perpetually evolving systems is indispensable for individuals, businesses, and content creators endeavoring to prosper in the digital era. As we’ve delved into the core concepts, from crawling and indexing to ranking and relevance, it becomes apparent that search engines occupy the central position in our online experiences.